The Role of the Tax Function: WHY, WHAT, and HOW
WHY: The Importance of the Tax Function
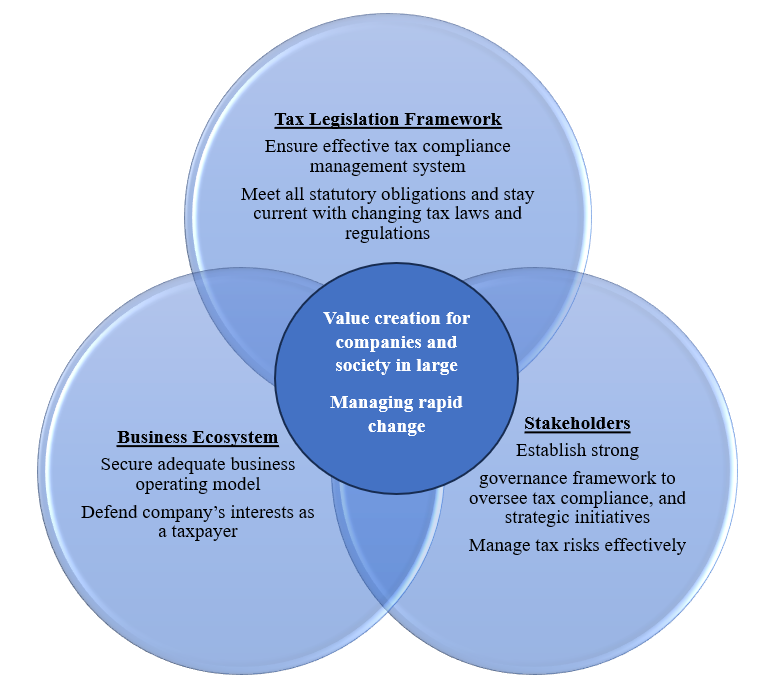
The tax function is crucial to an organization, influencing various aspects from effective business modelling to corporate image, compliance, and internal control. It also plays a significant role in change management programmes and the digital agenda of organization. Here is WHY the tax function matters:
1. Value Creation for Companies and Society in Large.
The tax function helps optimize tax positions across different jurisdictions, ensuring that company remains competitive and compliant. This optimization not only benefits the company but also contributes to the broader economic and social fabric by ensuring that taxes are paid fairly and efficiently.
2. Managing Rapid Change.
In a world where tax regulations are continually evolving, the tax function helps businesses adapt quickly. This adaptability is crucial for maintaining compliance and taking advantage of new opportunities or incentives that may arise from regulatory changes. Change could be represented by a new requirement, a new technology, a new market condition. The powerful management solutions of today are likely to be the disasters of tomorrow. Changes in the business environment might require different patterns of behaviour from the organization.
Figure 1
The importance of the Tax Function
WHAT: Key Responsibilities of the Tax Function
The tax function encompasses several critical responsibilities that ensure the organization's tax affairs are managed effectively:
1. Ensure Tax Compliance.
Meeting all statutory obligations and staying current with changing tax laws and regulations are fundamental.
2. Manage Tax Risks Effectively.
This involves defending the company’s interests as a taxpayer and ensuring that all tax-related risks are identified and mitigated.
3. Secure Adequate Business Modelling.
Ensuring that tax considerations are integrated into business models to optimize the overall tax position of the company.
HOW: Strategies and Methods for Effective Tax Management
1. Providing Information on Time, ensuring that all tax-related processes are completed on time, which includes filing returns and making payments within the stipulated deadlines.
Process Sourcing: Identifying and utilizing the best sources of tax-related processes to ensure accuracy and efficiency.
Data Mining: Extracting relevant tax data from various sources. Tax leaders have to step aside from the conventional notion that more information necessarily means greater control.
Data Analytics: Using advanced analytics to interpret tax data, identify trends, and make informed decisions. Tax leaders have to turn tax data into value.
Risk Management: Implementing strategies to identify, assess, and mitigate tax-related risks.
Response Time Tracking System: Establishing systems to track and improve the response time for tax-related queries and tasks.
2. Ensuring Quality of Tax Compliance Deliverables, ensuring that all tax filings and reports meet the highest standards of accuracy and completeness.
Responsibility Assignment Matrix (RACI): Clearly defining roles and responsibilities to ensure accountability in tax processes.
Compliance Calendar: Maintaining a detailed calendar to track all compliance deadlines and milestones.
Backup Matrix for Key Roles: Ensuring continuity by having backup personnel for critical tax arears and roles.
Internal Control System: Implementing robust internal controls to monitor and manage tax processes.
Tax Compliance Management System: Utilizing a dedicated system to manage compliance activities and ensure consistency.
Issue Resolution Path: Establishing clear protocols for addressing and resolving tax-related issues.
3. Building an Efficient Tax Compliance Process, continuously evaluating and improving tax processes to enhance efficiency and effectiveness.
Optimized Sourcing Strategy: Identifying the most cost-effective and reliable sources for tax data and compliance support.
Continuous Improvement Mindset: Encouraging a culture of continuous improvement within the tax function to adapt to changes and improve processes.
Digital Strategy: Leveraging technology to streamline tax processes, improve data accuracy, and reduce manual intervention.
Partnering (‘Open Book’) Operating Model with External Service Providers: Collaborating transparently with external tax advisors and service providers to enhance capabilities and efficiency.
Governance Ecosystem: Establishing a strong governance framework to oversee tax compliance, risk management, and strategic initiatives.
In conclusion, by focusing on WHY, WHAT, and HOW elements, the tax function can not only ensure compliance but also drive value creation and strategic advantage for the organization. Further, it helps tax leaders shift a focus from operating expenses to the tax function operating model, join the pieces into a wholistic end-to-end picture. Importantly, tax leaders must constantly scrutinize HOW solutions, encouraging a culture of continuous improvement within the tax function to adapt to changes and improve processes. In a process of ongoing development, tax leaders can never sit back on their laurels. As a result, considerable value will be created and long-term benefits delivered.