The Role of the Global Tax Process Owner
Introduction
In today’s complex and interconnected business landscape, the role of the Global Tax Process Owner (GPO) has become essential, especially in large multinational corporations. While companies of all sizes and industries can benefit from tax process oversight, global tax process ownership is particularly valuable in organizations that operate across numerous geographical locations and business units. The rapid pace of regulatory changes—including the implementation of Pillar 2, Country-by-Country Reporting (CbCR), and proposals like VAT in the Digital Age (ViDA)—alongside the complexity of compliance in various jurisdictions, has shifted the approach that corporations must take to manage their tax obligations. This evolution has placed the GPO at the center of corporate tax management, responsible for aligning global tax processes with corporate strategy, ensuring compliance, and fostering efficiency across borders.
The Responsibilities of the Global Tax Process Owner
Global Tax Process Owners play a vital role in both strategic and operational tax functions. Their responsibilities include defining and implementing tax strategies that align with the company's strategic objectives, analyzing national and international tax developments for relevance, and educating stakeholders on tax-relevant processes. They help create awareness of tax issues throughout the organization, making tax considerations a core component of business decision-making.
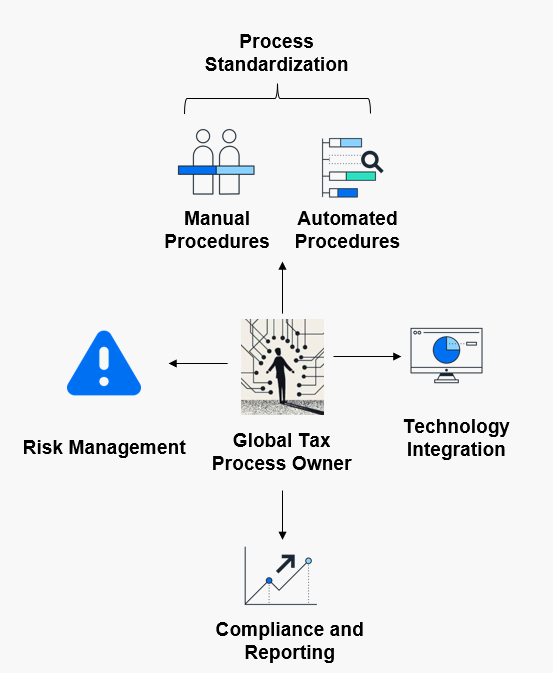
As illustrated in Figure 1, the key responsibilities of the Global Tax Process Owner span several core areas, each contributing to a well-governed, efficient, and compliant tax function.
Figure 1 The key responsibilities of the Global Tax Process Owner
Process Standardization
One of the primary roles of the GPO is to ensure the standardization and harmonization of tax processes across the organization. This entails designing, governing, and implementing processes on a global scale, in coordination with functional process owners and the centralized Tax Centre of Expertise. By leading efforts to standardize processes, the GPO helps reduce inefficiencies and establish best practices. The standardization of processes not only improves compliance and agility but also drives tax process excellence, which enhances the overall efficiency of the tax function within the organization.
Through close collaboration with other departments, the GPO can harmonize procedures across various tax domains, including direct tax, indirect tax, wage tax, and transfer pricing. This comprehensive approach ensures consistency and efficiency, allowing the company to operate seamlessly in multiple jurisdictions while maintaining compliance with local regulations.
Technology Integration
As tax regulations and operational requirements evolve, the integration of advanced technologies becomes increasingly crucial. GPOs play an integral role in selecting and implementing tax IT tools that enhance efficiency, accuracy, and compliance. They collaborate closely with IT departments to ensure that tax-specific requirements are met and oversee the implementation of technology projects that streamline tax processes.
A GPO’s involvement in technology extends to managing software deployments that drive automation and digital transformation within the tax function. This includes selecting platforms for real-time tax data analysis, implementing automation in compliance workflows, and ensuring that tax technology systems are aligned with the broader IT infrastructure of the organization. By doing so, GPOs ensure that tax functions are resilient, adaptable, and able to respond to regulatory changes swiftly.
Compliance and Reporting
In a world where tax regulations are increasingly stringent, GPOs must stay ahead of regulatory changes and anticipate shifts that could affect compliance requirements. They continuously assess the global tax landscape, providing insights to ensure that tax compliance processes are robust and capable of meeting new regulatory standards. Their analysis of tax data also serves broader business objectives, providing valuable insights for strategic decisions related to market entry, operational restructuring, and overall business strategy.
Additionally, GPOs manage the organization's tax compliance calendar and reporting obligations, ensuring that all tax filings are accurate and timely. By overseeing compliance processes at a global level, GPOs reduce the risk of penalties and improve the organization's overall tax standing.
Risk Management
A fundamental aspect of the GPO’s role is identifying and managing tax-related risks. They are responsible for implementing a group-wide tax risk management system, which may be part of a broader Tax Compliance Management System (Tax CMS). This includes developing mechanisms to automate compliance processes, identify bottlenecks, and redesign workflows to strengthen internal controls.
By embedding risk management into tax processes, GPOs protect the organization from exposure to regulatory, financial, and operational risks. Their work enables proactive management of risks, allowing the organization to respond quickly and effectively to potential compliance issues or process inefficiencies.
Collaboration with Key Stakeholders
The Global Tax Process Owner works closely with multiple stakeholders to ensure that tax processes are aligned with the overall business strategy and that tax considerations are integrated into daily operations. Figure 2 highlights the key stakeholders of the tax function involved in this collaboration.
Figure 2 Collaboration with key stakeholders
Functional Process Owners: Accountable for process performance and responsible for maintaining corporate tax expertise.
Tax Centre of Expertise: Responsible for executing tax processes and conducting quality assurance measures.
This collaborative framework fosters an integrated approach to tax management, where each stakeholder plays a defined role in ensuring smooth and efficient tax operations.
Conclusion
Global Tax Process Owners are critical to the effective management of tax processes within international corporations. Their roles in process standardization, technology integration, compliance, and risk management make them integral to an organization’s success. By overseeing tax process excellence, GPOs help businesses maintain compliance, drive operational efficiency, and adapt to a constantly evolving regulatory landscape. The strategic contributions of the GPO ultimately add substantial value, enabling organizations to navigate the complexities of global tax management with confidence and agility.